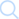
On December 23, the Seismological Working Group of the National Disaster Research Institute (NDI) continued its investigation in the extreme seismic area of the Jishishan M6.2 earthquake in Gansu province, and found a surface rupture zone near Yinjiashan, Dadun village, Dahejia Town.
The deformation zone is composed of many surface fissures and shows the characteristics of distributed deformation. It is distributed in the north-south direction, with steep cross-section and small reverse scarps. Along the staggered roads, farmland, ridges and so on. Tracking along both ends of the deformation belt, the south end gradually disappears into the valley. In the north direction, the main body of the deformation zone cuts through the ridge at a small angle, causing local landslides on the east side of the ridge. The discovered deformation zone is nearly 1km long and has good linearity. It crosses mountains in plane and is not controlled by topography. Compared with the regional survey data, it is basically consistent with the Yinjiashan reverse fault on 1:250000 map. In contrast to the distribution of the faults in the fifth generation map, it is located to the east of the southern margin of the Laggi Mountain.
According to the preliminary judgment of the working group, the deformation zone was caused by the surface rupture caused by the earthquake, which is basically consistent with the deformation characteristics shown by the macroscopic epicenter and Insar results calculated by Landsat-1. According to the fault mark of local reverse scarp, the maximum vertical displacement is about 8cm, and the maximum horizontal dislocation is about 2cm.